Business in Benin, Cotonou, Porto Novo
Benin: trade with Nigeria, informal sector, Logistics. Beninese Economy
Benin: an economy based on the informal sector
The economy of Benin (Africa) is characterized by a labour market dominated by the informal sector, which involves 95% of the working population and performs a major position in revenue generation
Top Beninese economic sectors are agricultural and cotton production, Road infrastructure, port activities, and general construction work
Beninese Banking sector: 2.5% growth (driven by International Trade with Nigeria)

- Introduction to the Republic of Benin (West Africa)
- Beninese Economy
- International Trade of Benin
- Port of Cotonou
- Business and Investment Opportunities in Benin
- Beninese Agriculture sector
- Mines and Hydrocarbons
- Tourism
- Infrastructure
- Transport and Logistics
- Access to the Beninese market
- Business Plan for Benin
Sample:

The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Benin” are:
- To analyze the Beninese Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in Benin
- To explore the Beninese trade relations with the student's country
- To develop a business plan for the Beninese market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Benin” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate in African Business.

Master in Business in Africa, Transport and Logistics in Africa.

Languages:  or
or  Bénin
Bénin  Benin
Benin  Benin.
Benin.
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in Benin”: 2

International Trade, Logistics and Business in Benin.

- Port of Cotonou
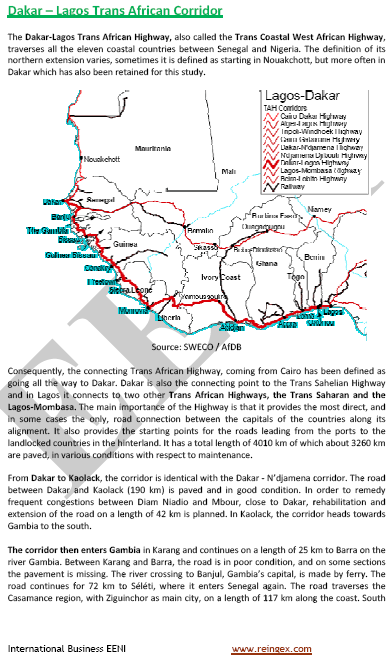
- Dakar-Benin-Lagos Logistics Corridor
- Benin-Niger-Burkina Faso-Ivory Coast Railway loop


Beninese Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Benin and the West African Economic Area
- Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
- West African Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU)
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- African Continental Free Trade Area
- Islamic Trade Preferential System
- Niger Basin Authority
- Harmonization of Business Law in Africa (OHADA)
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- The United States-Benin:
- AGOA (U.S.)
- US-WAEMU Agreement
- European Union-Benin:

- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on the Application of Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention
- Rotterdam Rules

- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Union
- AU Convention on Preventing and Combating Corruption
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Africa Agriculture Development Programme
- African Development Bank
- Africa-India Cooperation
- Africa-BRICS
- Africa-Turkey Partnership
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- China-Africa Cooperation

- Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC)
- Islamic Development Bank
- Afro-Arab Cooperation
- Arab Bank for Africa (BADEA)

Global Economic Organizations of Benin
- United Nations
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
- Cotonou is the economic capital of Benin
- Porto-Novo, the administrative capital of Benin, is the second-largest Beninese city (232,000 people)
- Largest cities: Cotonou, Porto-Novo, Abomey-Calavi, Djougou, Kétou, and Parakou
- Borders of Benin: Niger, Burkina Faso, Togo, and Nigeria
- Beninese Area: 112,622 km²
- Beninese Population: 10.3 million people
- Official language of Benin: French
- Local Beninese languages: Fon, Yoruba, and Nagot
More information about Benin (EENI African Business Portal).
Main religions in Benin:
- Christianity (Catholicism: 1.7 million)
- African Traditional Religions
- Islam

Benin belongs to the West African Economic Area.

Beninese Economy:
- Cotonou is the economic capital of Benin
- Porto-Novo, the administrative capital, is the second largest city (232,000 people)
- Top exports of Bebin: raw cotton (80%), groundnuts, and palm oil
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page







 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
