Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT)
Analysis of WTO Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade

With the objective that technical regulations (mandatory requirements), standards and conformity assessment procedures do not create Technical Barriers to Trade, nor that are discriminatory between the countries, the World Trade Organization (WTO) created the Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (OTC).
This agreement is binding for all the member countries of WTO.
The Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) belongs to agreements on Non-tariff Measures of WTO.
- Introduction to WTO Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT)
- Technical regulations
- Standards
- Conformity assessment procedures
- Technical Barriers to Trade- Information Management System (TBT IMS)
- Analysis of WTO Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT)
- Legal text of the Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Trade Restrictions
Sample - Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT):
The educational aims of the Subject “Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT)” are:
- Understand the pillars of WTO Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT)
- Know the concepts of Technical regulations, Standards and Conformity assessment procedures
- An In-depth analysis of the Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) to evaluate the implications for an exporting company

The Subject “WTO Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT)” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Courses: Non-tariff Measures, Foreign Trade Management.

Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade, International Transport.


Learning materials in

 Acuerdo sobre Obstáculos Técnicos al Comercio (OTC)
Acuerdo sobre Obstáculos Técnicos al Comercio (OTC)
 Accord sur les obstacles techniques au commerce (OTC)
Accord sur les obstacles techniques au commerce (OTC)  Acordo sobre as Barreiras Técnicas ao Comércio (OTC).
Acordo sobre as Barreiras Técnicas ao Comércio (OTC).
Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT).
The Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade is in force since 1995, applies to trade in goods (not applicable to Trade in Services).
The agreement does not cover issues related to Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures, regulated by the Agreement on the Application of Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures. Both agreements are related.
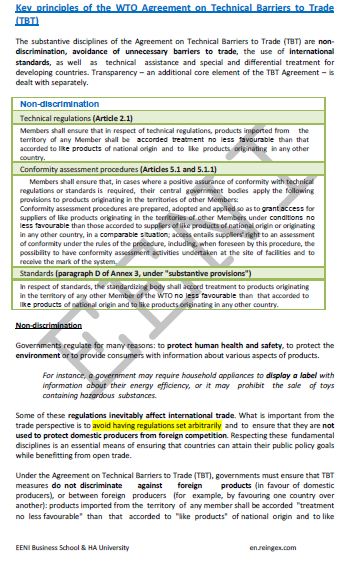
Like other agreements of WTO, the principles of non-discrimination, predictability in market access or preferential treatment for Developing Countries are the pillars of the Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT).
The TBT Committee of WTO is the body in charge of examining the special measures applied by Governments as well as facilitating implementation of the agreement.
Non-tariff Measures:
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page










 WhatsApp
WhatsApp