Business in Togo. Port of Lomé (Logistics)
Togo: access to West African landlocked countries (Foreign Trade). Phosphates
Togolese Republic: phosphates, agriculture, and Port of Lomé.
- The two pillars of the Togolese economy are agricultural sector (cotton, coffee, and cocoa) and phosphate industry
- Togo is self-sufficient in agricultural export products
- The Port of Lomé is one of the largest in West Africa and one of the safest and the most efficient port in the Gulf of Guinea

Togo: an strategic position in West Africa. Access to the West African landlocked countries.
- Introduction to the Togolese Republic (West Africa)
- Togolese Economy
- International Trade of Togo
- Transport and Logistics
- Business and Investment Opportunities in Togo
- Investment in Togo
- Access to the Togolese market
- Business Plan for Togo
Sample:

The objectives of the subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in the Togolese Republic” are:
- To analyze the Togolese Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in the Togolese Republic
- To explore the Togolese trade relations with the student's country
- To learn about Togolese Trade Agreements
- To develop a business plan for the Togolese market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Togo” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate in African Business.

Master in Business in Africa, International Business.

- Subject Credits “Doing Business in Togo”: 1

Area of Knowledge: Africa.
International Trade, Logistics and Business in Togo - Lomé

- Autonomous Port of Lomé
- Togo Free Zone
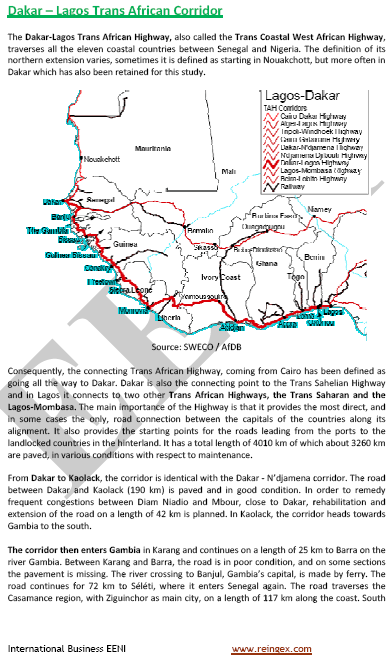
- Access to the Dakar-Lagos Logistics Corridor


Togolese Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Togo and the West African Economic Area
- Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
- West African Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU)
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- African Continental Free Trade Area
- The United States-Togo
- AGOA (U.S.)
- US-WAEMU Agreement
- European Union-Togo
- GSP
- Africa-EU Partnership
- Harmonization of Business Law in Africa (OHADA)
- Islamic Trade Preferential System
- Arab Bank for Africa (BADEA)

- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention
- Rotterdam Rules

- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Union
- AU Convention on Combating Corruption
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Africa Agriculture Development Programme
- African Development Bank
- China-Africa Cooperation
- Africa-India Cooperation
- Africa-BRICS
- Africa-Japan Cooperation
- Africa-South America Summit

- Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC)
- Afro-Arab Cooperation
- Arab Bank for Africa (BADEA)

- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
- United Nations
- The Togolese Republic enjoys a strategic position in the West African region
- Togolese Population: 7.6 million people
- Area of Togo: 56,785 km²
- Capital of Togo: Lomé (1,900,283 people)
- Togo shares borders with Burkina Faso, Benin, and Ghana
- Official language of Togo: French
- Togolese Independence: 1960 (France)
More information about Togo (EENI African Business Portal).
Main religions in Togo:
- Christianity
- Islam (20% of the Togolese population, 1.1 million)
- African Traditional Religions

Togo belongs to the West African Economic Area.

- Togolese Agriculture: 65% of the labour force
- Cotton, coffee, and cocoa represent 40% of total Togolese exports
- Top Togolese trade partners: Burkina Faso, Ghana, the Netherlands, Benin, Mali, and Ivory Coast
- Most dynamic Togolese sectors: retail, transportation, and communications
- Togo is the fourth larger phosphate producer in the World
- Togolese Currency: Franc CFA
Togo Telecom is a corporation created by the split of the OPTT two State-owned enterprises. It is governed by Act No. 90-26 of December 4, 1990, to reform the legal and institutional framework for the Public Enterprises. It has a legal personality and financial autonomy, with a capital of 4 billion CFA francs.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page








 WhatsApp
WhatsApp

 or
or 

