Trans-Caspian Trade and Transit Corridor, Turkey
Transport Corridor (Trans-Caspian) Azerbaijan, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan
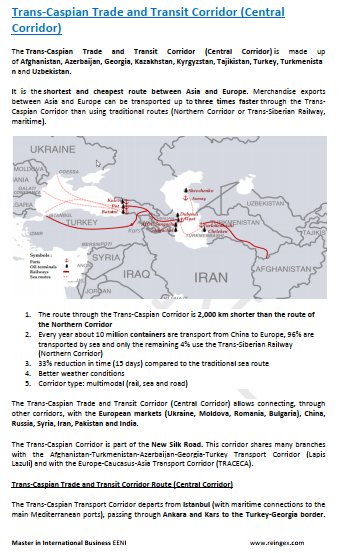
The Trans-Caspian Trade and Transit Corridor (Central Corridor) is made up of Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkey, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan.
It is the shortest and cheapest route between Asia and Europe. Merchandise exports between Asia and Europe can be transported up to three times faster through the Trans-Caspian Corridor than using traditional routes (Northern Corridor or Trans-Siberian Railway, maritime).
The route through the Trans-Caspian Corridor is 2,000 km shorter than the route of the Northern Corridor

Trans-European Transport Corridors
- Introduction to the Trans-Caspian Trade and Transit Corridor (Central Corridor): the shortest route between Asia and Europe
- Member countries of the corridor: Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkey, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan
- Main features of the Trans-Caspian Corridor
- The Trans-Caspian Corridor and its relationship with the
- Countries in the influence area of the Trans-Caspian Corridor: Ukraine, Moldova, Romania, Bulgaria, China, Russia, Syria, Iran, Pakistan and India
- The Trans-Caspian Corridor as part of the Silk Road of the 21st century
Sample - Corridor
Trans-Caspian (Central Corridor)

The Subject «Trans-Caspian Trade and Transit Corridor (Central Corridor)» is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Transportation Courses: Road Transport, Railway, Multimodal.

Certificate in International Transport

Masters: International Transport, International Business.


Languages:  .
Summary in
.
Summary in  Corredor Transcaspiano
Corredor Transcaspiano
 Corridor transcaspien (Central Corridor)
Corridor transcaspien (Central Corridor)  Corredor Trans-Caspiano (Corredor Central).
Corredor Trans-Caspiano (Corredor Central).

Trans-Caspian Trade and Transit Corridor (Central Corridor).
- Every year about 10 million Containers are transport from China to Europe, 96% are transported by sea and only the remaining 4% use the Trans-Siberian Railway (Northern Corridor)
- 33% reduction in time (15 days) compared to the traditional sea route
- Better weather conditions
- Corridor type: multimodal (rail, sea and road)
The Trans-Caspian Trade and Transit Corridor (Central Corridor) allows connecting, through other corridors, with the European markets (Ukraine, Moldova, Romania, Bulgaria), China, Russia, Syria, Iran, Pakistan and India.
The Trans-Caspian Corridor is part of the New Silk Road. This
corridor shares many branches with the Afghanistan-Turkmenistan-Azerbaijan-Georgia-Turkey Transport Corridor (Lapis
Lazuli) and with the Europe-Caucasus-Asia Transport Corridor (TRACECA).
The transportation of oil and petrochemical products from the Central Asian republics make this corridor a strategic objective for many countries,
both in the region and for China or the United States.
Trans-Caspian Trade and Transit Corridor Route (Central Corridor)
The Trans-Caspian Transport Corridor departs from Istanbul (with maritime connections to the main Mediterranean ports), passing through Ankara and Kars to the Turkey-Georgia border.
In Georgia the corridor accesses the ports of Pod, Kulevi and Batumi (Black
Sea, access to Bulgaria, Romania and Moldova). By road the Georgia-Azerbaijan border is reached, passing through Tbilisi (Capital of Georgia)
sharing a route with the Afghanistan-Turkmenistan-Azerbaijan-Georgia-Turkey
Transport Corridor (Lapis Lazuli). Access to the ports of Ayat and Baku.
From Baku (Capital of Azerbaijan) the Caspian Sea is crossed to Turkmenbashi (Turkmenistan). From Baku there are maritime connections
for Aktau and Kuryk (Kazakhstan)
From Turkmenbashi (Turkmenistan) a road leaves that passing through Ashgabat reaches the Turkmenistan-Afghanistan border
It passes by rail and road, respectively, through Georgia, Azerbaijan, and the Caspian Sea (crossing the Caspian transit corridor) and reaches China following the Turkmenistan-Uzbekistan-Kyrgyzstan or Kazakhstan route.
Asian regional economic communities related to the Trans-Caspian Trade and Transit Corridor (Central Corridor).
- Central Asia Cooperation (CAREC): Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, Pakistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan
- Eurasian Economic Union: Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Russia
- Shanghai Cooperation Organization: Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan
- Economic Cooperation Organization (ECO): Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Iran, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Pakistan, Tajikistan, Turkey, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan
- Commonwealth of Independent States: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Russia, Ukraine, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan
- Turkic Council: Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Turkey
- Organization for Cooperation between Railways (OSJD): Azerbaijan, Albania, Afghanistan, Belarus, Bulgaria, Hungary, Vietnam, Georgia, Iran, Kazakhstan, China, North Korea, South Korea, Cuba, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lithuania, Moldova, Mongolia, Poland, Russia, Romania, Slovakia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Ukraine, Czech Republic and Estonia
- Organization for Democracy and Economic Development (GUAM): Azerbaijan, Georgia, Moldova and Ukraine
- Black Sea Cooperation: Albania, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bulgaria, Georgia, Greece, Moldova, Romania, Russia, Turkey and Belarus
- EU Eastern Partnership: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Moldova and Ukraine
- European Union-South Caucasus Relations: Armenia, Azerbaijan and Georgia
- European Neighborhood Policy: Algeria, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Egypt, Georgia, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Libya, Moldova, Morocco, the Occupied Palestinian Territory, Syria, Tunisia and Ukraine
- Black Sea Synergy: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Moldova, Russia, Turkey and Ukraine
- Turkey is a member of:
- Euro-Mediterranean Partnership
- Customs Union with the European Union
- Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)
- Africa-Turkey Partnership
- Turkey is an observer country at the ACS
Related Trade Agreements
- Kazakhstan
- Customs Union with Russia and Belarus
- Trade Agreements with Armenia, Ukraine and Georgia
- Enhanced Partnership and Cooperation Agreement with the European Union
- Kyrgyzstan
- Trade and Economic Cooperation Agreement with Pakistan
- Trade Agreements with Armenia, Moldova, Ukraine and Uzbekistan
- Tajikistan
- Trade Agreements with Armenia, Ukraine and with the Eurasian Economic Union
- Turkmenistan
- Trade Agreements with Armenia, Georgia and with the Eurasian Economic Union
- Azerbaijan
- Trade Agreements with Russia, Ukraine and Georgia
- Free Trade Agreement between Georgia, Ukraine, Azerbaijan and Moldova
- The European Union Eastern Partnership
- Georgia
- European Union-Georgia Agreement
- EFTA-Georgia Agreement
- Trade Agreements of Georgia with Turkey, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Russia, Ukraine, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan
- Free Trade Agreement between Georgia, Ukraine, Azerbaijan and Moldova
- Turkey
- Turkish Trade Agreements: EFTA, Tunisia, Egypt, the EU, Chile, Africa-Turkey, Israel, Macedonia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Palestine, Syria, Jordan, Georgia and Albania
- Islamic Trade Preferential System (TPS-OIC)
Main Euro-Asian institutions related to the Corridor
- Boao Forum for Asia
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue
- Economic Commission for Asia (ESCAP)
- Asian Development Bank
- Colombo Plan
- Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE)
Major Islamic institutions related to the corridor
- OCI
- Islamic Development Bank
The main Religions of the region of the Transport Corridor Trans-Caspian (Central Corridor) are:
The Trans-Caspian Trade and Transit Corridor (Central Corridor) belongs to the:
Related Corridors to the Silk Road
- Bangladesh-Myanmar Logistics Corridor
- Asia-Africa Logistics Corridor
- China-Central-West Asia Logistics Corridor
- China-Russia Logistics Corridor
- International North-South Logistics Corridor
- Kyrgyzstan-Iran Logistics Corridor
- Corridor of the Ashgabat Agreement
- Trans-Siberian Railway (Russia, North Korea)
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page










 WhatsApp
WhatsApp