Intercultural Management, Cross-cultural Communication
High and Low context culture (Cross-cultural Management) Marketing strategies
Intercultural Negotiation is one of the most important and challenging aspects of International Trade.
Religion impacts on many areas of International Marketing. It can restrict the types of products / services that consumers may purchase or use. It also influences on how products are promoted.

Religions and Global Business -
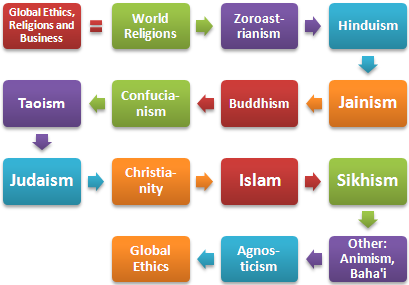
Religious diversity
- Introduction to Cross-cultural Management
- Culture and global society
- High and low context cultures (Edward Hall)
- Cultural dimension (Hofstede): Power distance, Individual, and Long-Term Orientation
- Trompenaars' Seven Dimensions
- Cross-cultural communication and International Marketing Plan
- Cross-cultural Management and International Business
- Cultural patterns and markets
- Countries classification
- Key strategies for dealing with new cultures
- Case Study:
- Perception of Ceramic tiles in different markets
- Hofstede Dimensions and World's Religions
- McDonald’s in India – A Cross-Cultural Management Success Story
- Cross-Cultural Management and Globalization
- Introduction to
Religions and Business
- Cultural influence of religion in global business
- Religion and international contracts
- Religious risks for the global enterprise
- Case Study: Religious Diversity in a Multinational Company (TechGlobal)
Sample - Cross-cultural Management:

The main objective of the Subject “Cross-cultural Management” is to gain an understanding of the nature of different cultures and how to adapt strategies of International Marketing to different countries.
In this subject, student will learn about adapting global marketing approach to different markets.
This will be achieved by:
- Examining how the diversity of culture can influence the outcome of an International Marketing Plan
- Outlining the key strategies to dealing with new cultures
- Detailing the major theories on Intercultural Management
- Highlighting the critical errors to be avoided when dealing with different cultures

The Subject “Cross-cultural Management” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Masters: Foreign Trade, International Business.

Postgraduate Certificate in Global Marketing.

Doctorate: Ethics, Religion & Business, World Trade.

Languages:  or
or  Négociation Interculturelle
Négociation Interculturelle  Negociacion intercultural
Negociacion intercultural  Negociação intercultural.
Negociação intercultural.
- Subject Credits “Cross-cultural Management”: 3

Area of Knowledge: Internationalization.
Exporter negotiates with individuals from countries with different cultures and habits. If the exporter does not adopt an open and respectful attitude towards these cultures; he will hardly achieve the success in his business. He should try to learn the idiosyncrasies of each market.
The self-reference criterion (James A Lee) as an unconscious reference to one's cultural values, experiences, and knowledge as a basis for decisions. The self-reference criterion impedes the ability to assess a foreign market in its true light.
Edward Hall divides cultures into two types, according to its context:
- High-context culture.
- Context rather than content is of significance
- Fewer legal documents are used in these cultures, where one's word is one's bond, and this makes negotiations a lot slower
- Social position is also a dominant factor
- Japan and the Arab Countries are examples of these culture
- Low-context culture.
- With clear and explicit messages in which, written words transmit most of information
- Legal documents are considered essential
- Europe and the United States are examples of these culture
Hofstede Theory is based on the assumption that countries can be compared to each other by rating the following parameters:
- Power Distance Orientation (distance from power)
- Individual vs. Collective Orientation
- Dominant Values Orientation (Masculinity or femininity)
- Uncertainty Avoidance Orientation (Distance from uncertainty)
- Short-Term vs. Long-Term Orientation
Trompenaars' Seven Dimensions
- Universalism vs. Particularism
- Individualism vs. Communitarianism
- Neutral vs. Emotional
- Specific vs. Diffuse
- Achievement vs. Ascription
- Sequential vs. Synchronic time
- Internal vs. External control
How to negotiate successfully in:
- America: Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Mexico, Uruguay, or Venezuela
- Africa: D.R. Congo, Morocco, Nigeria, or Senegal
- MENA- Middle East: Egypt, Saudi Arabia, or the United Arab Emirates
- Europe: Czech Republic, Portugal, or Russia
- Asia: China, India, Indonesia, Hong Kong, Japan, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, or Vietnam
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page










 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
