Hinduism, Businesspeople, Bhagavad Gita (India)
Ethical Principles of Hinduism: Non-Violence, Ethics, Bhagavad Gita, Sri Ramakrishna
“Truth is one; the wise call it by various names.” (Rig Veda).
Attempting to define Hinduism is a complex task, the correct term for Hinduism should be “Sanatana Dharma” or the Eternal Law.
According to Swami Vivekananda, the spiritual heir of Sri Ramakrishna:
“Hinduism is based on the accumulated treasure consisting of spiritual laws discovered by different people in different times.”

“Everyone should follow his religion. A Christian should follow Christianity; a Muslim should follow Islam, and so on. For Hinduism, the old way, the way of the Aryan wises is the best.” Sri Ramakrishna.
Hinduism, with 1.2 billion followers, primarily influences India, Nepal, and diaspora communities (Bhutan, Mauritius), influencing business through its cultural and religious practices.
India is a global leader in the Ayurvedic products market, which includes medicines, cosmetics, and dietary supplements based on traditional Hindu natural medicine practices. This market, valued at over $10 billion in 2023, is experiencing growing demand in countries such as the United States, Europe, and Southeast Asia. Hindu principles such as ahimsa (nonviolence), satya (truth), and sustainability influence the production, marketing, and financing of these products, promoting ethical and environmentally friendly business practices.

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
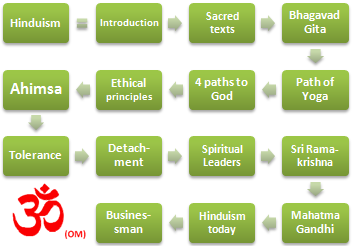
The Subject “Hinduism, Ethics and Business” consists of three parts:
- Introduction to Hinduism
- Hindu Businesspeople
- Hindu Economic Area
- Introduction to Hinduism - “Sanatana Dharma” (Eternal Religion) - Vedanta
- Sacred Texts of Hinduism (Shruti and Smriti)
- Bhagavad Gita
- Four Paths to God
- Paths of Yoga
- Key concepts related to Hinduism:
- Interreligious Tolerance
- Body and Atman
- Samsara
- Good (Svayam Bhagavan, Parabrahman) Pervades all Things
- Ethical Principles of Hinduism:
- Non-Violence (Ahimsa)
- Truth (Satya)
- Not to steal (Asteya)
- Sexual moderation (Brahmacharya)
- Detachment from the results of actions
- Main traditions of Hinduism (Sampradaya)
- Vaishnavism
- Shaivism
- Shaktism
- Smartism
- Renewal of Hinduism:
- Sri Ramakrishna
- Swami Vivekananda
- Mahatma Gandhi
- Hinduism today
- Ayurvedic products market
- Hinduism in Nepal, Bhutan, and Mauritius
Renewal of Hinduism:
Sri Ramakrishna


Case study: Hindu Businesspeople (Hinduism)

- Introduction to the Hindu Economic Area
- Influence of Hinduism, Jainism, Sikhism, and Zoroastrianism on Hindu Civilization
- Area of influence of Hindu Civilization: Nepal, Mauritius, Bhutan, Indonesia, and East Africa
- Interactions of Hindu Civilization with other civilizations

The educational aims of the Subject “Hinduism, Ethics and Business” are the following:
- To understand the fundamentals of Hinduism
- To understand the ethical principles of Hinduism
- To analyze the figures of Hindu Businesspeople
- To learn about the influence of Hinduism on business
- To understand the influence of Hinduism on Hindu Civilization
- To explore the economic relations of Hindu Civilization with other civilizations
- To learn about countries of influence of Hindu Civilization

The Subject “Hinduism, Ethics and Business” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Bhagavad Gita Courses, Realization of the Gita
Masters: International Business, Religions and Business.

Doctorate: Global Ethics, Religions, and International Business, World Trade.
 Masters adapted to Indian Students (Bharat).
Masters adapted to Indian Students (Bharat).
Languages:  (or
(or  Hinduismo
Hinduismo  Hindouisme
Hindouisme  Hinduísmo).
Hinduísmo).
- Subject Credits “Indian Religions - Hinduism”: 4

- Duration: 4 weeks
- Download the syllabus: “Indian Religions” (PDF)


The difficulty of finding a proper definition is that Hinduism has no central doctrinal authority (similar to the papacy in Catholicism), but they have swamis (teachers) or gurus (spiritual guides).
Today; it is common to identify different types of Hinduism:
- Vedanta
- Vaishnavism
- Shaivism
- Shaktism
- Smartism
The appellations are based primarily on the god worshipped as an absolute reality and traditions that accompany worship of that God.
The vast majority of Hindus claim that Hinduism is monotheistic, claiming that Hindu pantheon is only the representations of one God to facilitate human understanding of the Absolute Reality.
Hinduism is a Wisdom Tradition that evolves periodically throughout the history. “Live and let live” defines relatively well the vision of Hinduism.
Hinduism is probably the most tolerant religion with others, as seen in the history of India in the last 2500 years. Hinduism has lived with Parsees, Sikhs, Muslims, Christians, Buddhists, and Jain.
Chapter IV of the Bhagavad Gita begins with one of the most beautiful and transcendental verses of the Bhagavad Gita, which appreciate the tolerance of Hinduism with other religions:
“When the kindness declines, When the wickedness increases
When the purpose of the life is forgotten.
I will manifest, I will return.
To pronounce the sacred; to destroy the sin of the sinner, to re-establish the way of the principles” Bhagavad Gita IV-
Yoga of Knowledge and Renunciation of Action 7-8
- About 950 million people practice Hinduism, mainly in India (Bharat)
- Hinduism is the third religion in the World by the number of believers, behind Islam and Christianity
The Absolute Reality of Hinduism is Brahman. The Hindus believe in the reincarnation and law of Karma.
Hinduism proposes different ways to reach God (the path of love, Devotion, knowledge) depending on each person.

The Ethical Principles of Hinduism: Ahimsa (Non-Violence), detachment (abandonment of the fruits of the action), Truthfulness, Not to steal, Self-control, discipline, appropriate words and thoughts, and motivation to achieve the goal.
The principle of Non-Violence (Ahimsa) should be one of the pillars of a global ethic. All religions also share the Ahimsa Principle especially Jain, Zoroastrians, and Buddhists.
Patanjali suggests the ethical practice of five exercises: ahimsa, truthfulness, non-stealing, pure life and not greed. This is widely reflected in the Bhagavad Gita.
Previously we have seen several Hinduism values: Ahimsa (non-violence), tolerance, and truthfulness. All of which are part of the five Yamas (restraints or abstentions) and five Niyamas (observances or rules) set by Patanjali.
Yamas (restraints or abstentions).
- Non-Violence (Ahimsa)
- Truthfulness (Satya)
- Not to steal (Asteya)
- Sexual Moderation (Brahmacharya: observance of the fundamental vows)
- Non-possession (Aparigraha)
Niyamas (Observances).
- Purity (Shauca)
- Satisfaction (Santosa)
- Austerity/Self-discipline (Tapas)
- Self-knowledge (Svadhyaya)
- Surrendering to God (Ishvarapranidhana)

Diwali, the Hindu festival of lights, generates $70 billion in spending on gold, electronics, and clothing in India (FICCI, 2024). Retailers like Reliance offer Diwali-specific discounts, increasing sales by 15%.
Hindu dietary restrictions create a $30 billion vegetarian food market in India (IMARC Group, 2024). McDonald's India does not serve beef or pork, and 70% of its menu is vegetarian, contributing 25% of its regional revenue (Forbes, 2024).
Religions and Business - Zoroastrianism, Sikhism, Jainism, Buddhism.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page











 WhatsApp
WhatsApp

