World Customs Organization (WCO) Harmonized System
Custom valuation. Rules of origin. Trade Facilitation. SAFE Package
The World Customs Organization (WCO) is the sole intergovernmental body fully working on customs and International Trade (imports and exports).
The World Customs Organization (WCO) keeps the International Harmonized System products nomenclature and manages the technical aspects of WTO Agreements on Customs Valuation and Rules of Origin.
The World Customs Organization (WCO) has developed the Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System (Harmonized System - “HS”), an international product nomenclature. 98% of International Trade in Goods use the Harmonized System.
The members of WCO represent 98% of global trade.

- Introduction to the World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Harmonized System (HS) of WCO
- Customs Valuation
-
Rules of Origin
- Agreement on Rules of Origin of WTO
- Customs Enforcement and Compliance
- SAFE Package
- Customs Procedures and Trade Facilitation
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- Mercator program
- Trade Restrictions
- Conventions:
- Kyoto Convention (Containers)
- ATA System
- Istanbul Convention
- Customs Convention on Containers
- Case Study: market access map

The purposes of the subject “World Customs Organization (WCO)” are the following:
- To learn about role of WCO
- To understand the key concepts related to customs: non-tariff barriers, customs valuation, transaction value, previous inspection, rules of origin, and import licenses
- To learn about Harmonized System and existing conventions

The Subject “World Customs Organization (WCO)” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Postgraduate Certificate in International Trade.

Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade, International Transport.


Languages:  or
or  Organization mondiale des douanes
Organization mondiale des douanes  Organización Mundial de Aduanas
Organización Mundial de Aduanas  Organização Mundial das Alfândegas (OMA).
Organização Mundial das Alfândegas (OMA).

The World Customs Organization works in the following fields:
- International Trade standards development
- Simplification and harmonization of Customs Procedures (imports and exports)
- International Trade supply chain security
- International Trade Facilitation
- Customs enhancement and accordance activities, anti-counterfeiting and piracy initiatives
Sample: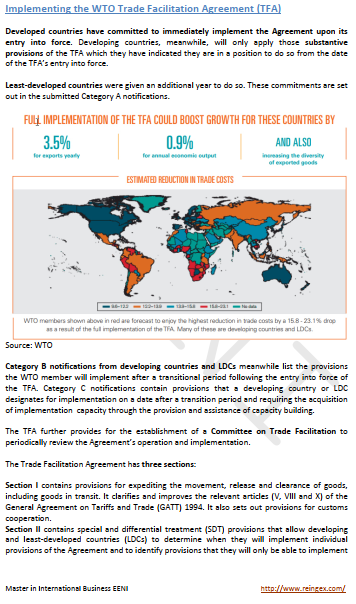
The BIC Code (International Identification Codes of Container Owners) is accepted by the World Customs Organization (WCO):

- Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures
- Technical Barriers to Trade
- Pre-shipment Inspection
- Anti-dumping Measures and Safeguards
- Import Licensing and Quotas
Sample: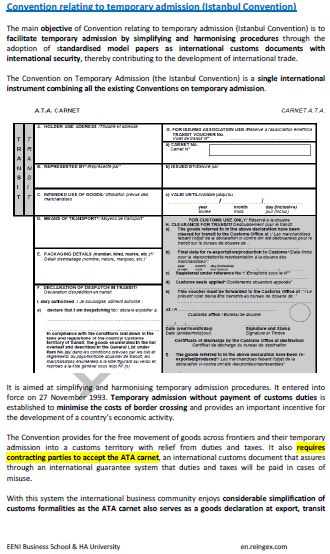
The World Customs Organization (WCO) member countries are:
The European Union, The customs territories of Netherlands Antilles, Bermuda, Hong Kong and Macau, Albania, Algeria, Andorra, Angola, Argentina, Armenia, Australia, Austria, Azerbaijan, the Bahamas, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Barbados, Belarus, Belgium, Benin, Bhutan, Bolivia, Botswana, Brazil, Brunei, Bulgaria, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cambodia, Cameroon, Canada, Cape Verde, Central African Republic, Chile, People's Republic of China, Colombia, The Comoros, the Republic of the Congo, Costa Rica, Ivory Coast, Croatia, Cuba, Cyprus, The Czech Republic, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Denmark, Ecuador, Egypt, El Salvador, Eritrea, Estonia, Ethiopia, Fiji, Finland, Republic of Macedonia, France, Gabon, The Gambia, Georgia, Germany, Ghana, Greece, Guatemala, Guinea, Guyana, Haiti, Honduras, Hungary, Iceland, India, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Jamaica, Japan, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kenya, South Korea, Kuwait, the Kyrgyz Republic, Latvia, Lebanon, Lesotho, Liberia, Libya, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Madagascar, Malawi, Malaysia, Maldives, Mali, Malta, Mauritania, Mauritius, Mexico, Moldova, Mongolia, Morocco, Mozambique, Myanmar, Namibia, Nepal, Netherlands, New Zealand, Nicaragua, Niger, Nigeria, Norway, Oman, Pakistan, Panama, Papua New Guinea, Paraguay, Peru, The Philippines, Poland, Portugal, Qatar, Romania, Russia, Rwanda, Samoa, São Tomé, Saudi Arabia, Senegal, Serbia, the Seychelles, Sierra Leone, Singapore, Slovakia, Slovenia, South Africa, Spain, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Suriname, Eswatini, Sweden, Switzerland, Syria, Tajikistan, Tanzania, Thailand, East Timor, Togo, Trinidad and Tobago, Tunisia, Turkey, Turkmenistan, Uganda, Ukraine, the Emirates, the UK, the United States, Uruguay, Uzbekistan, Venezuela, Vietnam, Yemen, Zambia, Zimbabwe.
No members Countries of WCO: Antigua and Barbuda, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Grenada, Dominica, Equatorial Guinea, Somalia, North Korea, Liechtenstein, Monaco, San Marino, Vatican City, Palau, Solomon Islands, Micronesia, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Tuvalu, Nauru, Cook Islands, Niue and Palestinian Authority, Taiwan, Sahrawi Republic, Kosovo.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page










 WhatsApp
WhatsApp