Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) WTO
Safeguard Measures, Technical barriers to trade. Anti-dumping

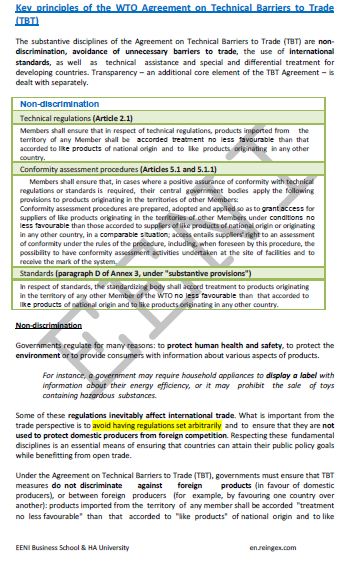
Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) are all those Non-tariff measures that are established through technical regulations and conformity assessment procedures (with these regulations and standards).
Sanitary and phytosanitary (SPS Agreement) measures are not considered as a Technical Barriers to Trade.
In Foreign Trade, a technical regulation is a document where the product characteristics and / or their related processes and production methods are defined.
- Introduction to Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT)
- Trade Restrictions
- Technical regulations (labeling, terminology...)
- Conformity assessment procedures (accreditation, sampling, inspection, registration, approval)
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
Sample - Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT):

The educational aims of the Subject “Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT)” are the following:
- To know how to identify and distinguish Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT)
- To evaluate the possible impact that these technical barriers to Foreign Trade may have on exports / imports
- To know how to act in the face of a technical barrier to trade established by a country

The Subject “Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT)” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade, International Transport.


Languages 
 Obstáculos técnicos al comercio
Obstáculos técnicos al comercio
 Obstacles techniques au commerce
Obstacles techniques au commerce  Barreiras técnicas ao comércio.
Barreiras técnicas ao comércio.
- Non-tariff Measures in Foreign Trade (Anti-dumping Measures and safeguards, Import license and contingents)
- Trade Facilitation - Trade Facilitation Agreement - Kyoto Convention (Containers) - Convention Harmonization of Frontier Controls of Goods

- Specifications of a technical regulation are mandatory
- Technical regulations may also contain rules on the labeling requirements, terminology, etc
To verify that the requirements of the technical regulation are met, the conformity assessment procedure is used. These procedures can be: accreditation, approval, sampling, inspection, registration...
The main Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) are the following:
Prohibitions or restrictions of imports of products for objectives set out in the Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT)
- Prohibitions for Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT)
- Authorization requirement for reasons of Technical Barriers to Trade
- Registration requirement for importers for reasons of technical barriers to trade
- Other requirements or prohibitions
Tolerance limits for residues and restricted use of substances:
- Residue tolerance limits or contamination by certain substances
- Restricted use of certain substances
Labeling, marking and packaging requirements:
- Labeling requirements
- Marking requirements for transport
- Requirements for goods packing
Production or post-production requirements:
- Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) regulations on production processes
- TBT regulations on transport and storage
- Other requirements
Product identity requirement (for example, organic or ecological labels).
Product-quality or performance requirement (durability, hardness, content of ingredients).
- Conformity assessment related to Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT)
- Product registration requirement
- Testing requirement (conformity)
- Certification requirement (according to a certain standard)
- Inspection requirement (in the importing country)
- Traceability information requirements (production, processing and distribution)
Pre-shipment Inspection (quality, export price, quantity)..
- Pre-shipment inspection
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Direct consignment requirement (prohibition of stopping at a third country)
- Requirement to pass through the specified port of customs
- Import-monitoring and surveillance requirements (automatic licensing process)
- Other formalities
Contingent trade-protective measures:
- Anti-dumping measures (import at a lower value than the market of origin). Investigation, anti-dumping duties, price undertakings
- Compensatory measures (at the border, related to subsidized exports). Investigation, countervailing duties, commitments
Safeguard (countervailing) Measures:
- General safeguard (multilateral, temporary suspension of multilateral concessions to protect the national industry)
- Research, Safeguard duties. Quantitative restrictions. Other types of safeguard measures
- Special safeguard for agriculture, based on the volume or price
Prohibitions and quantity-control measures other than Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS) or Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) reasons:
- Non-automatic import-licensing procedures other than authorizations for SPS or TBT reasons
- Licenses for economic reasons. Licenses for specific use. Licenses linked with local production
- Licenses for non-economic reasons. Licenses for religious, moral or cultural reasons. Licenses for political reasons
- Quotas (import restrictions). Permanent / Temporary (global allocation, by countries)
- Prohibitions for reasons other than SPS or TBT measures (economic reasons or not, import prohibition, seasonal ban)
- Export limitation agreements. Voluntary limitation of exports. Agreements on quotas, consultations, administrative cooperation
- Tariff quotas: consolidated in WTO, Countries / world allocation
Import price control measures (charges and additional taxes included. Para-tariff measures)
- Administrative measures that affect the customs value of a good (minimum and maximum prices, reference prices)
- Voluntary limitation of exports price
- Variable charges (Taxes, levies or variable components, additional customs duties)
- Customs surcharges (Taxes ad hoc imports)
- Seasonal rights (agricultural products)
- Additional taxes (related to the services provided by the State of the country of the Importer): inspection fees, storage, foreign exchange transactions, consular fees...
- Internal taxes and charges on imports (with national equivalence): Consumption taxes, special charges, sensitive products
- Values set by the customs administration (avoid fraud, protect the national industry)
Source: “International Classification of Non-tariff Measures”, UN Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD).
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page










 WhatsApp
WhatsApp