South Asian Association Regional Cooperation SAARC
South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA). Economic Union (Bangladesh, Bhutan, India...)

In 1985 was formed the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) by Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, the Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.
The objective of SAARC is to speeding up the economic and social development process

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
- Introduction to the South Asian Association Regional Cooperation (SAARC)
- Cooperation areas of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
- Economy
- International Trade
- Communications
- Transport and Logistics
- SAARC Preferential Trading Arrangement (SAPTA): Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka
- South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA)
- South Asian Economic Union
- International Trade in the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation region
- South Asia Economic Cooperation (SASEC)
Sample - South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC):

The educational aims of the Subject “South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation” are:
- To understand the purposes and functions of SAARC
- To assess the benefits for the member countries of SAARC and its cooperation areas
- To analyze the Free Trade Area (SAFTA) and the economic union of South Asia
- To explore Foreign Trade among the member countries of SAARC

The Subject “South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.


Course: Hinduism and Business.
Languages:  or
or  Asociación para la Cooperación Regional del Sur de Asia
Asociación para la Cooperación Regional del Sur de Asia  Association sud-asiatique pour la coopération régionale (ASACR)
Association sud-asiatique pour la coopération régionale (ASACR)  Associação Cooperação Regional Ásia do Sul.
Associação Cooperação Regional Ásia do Sul.
Credits of the Subject “South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)”:
1 

South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
The observer countries of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) are Australia, Japan, Iran, Mauritius, Myanmar, South Korea, the United States, and the European Union.
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC):
- 1.5 billion people (22% of the World's population)
- Foreign Trade of South Asia has been increasing at a faster rate (17%) than the world trade growth (11%)
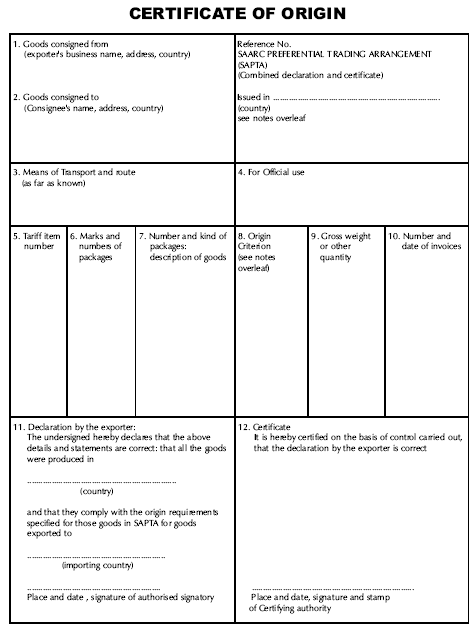
SAARC Preferential Trading Arrangement.
SAARC Preferential Trade Arrangement (SAPTA) was forecasted primarily as the first step towards the transition to a South Asian Free Trade Area leading subsequently, towards in a customs union, Common Market and an Economic Union.
- The South Asian Free Trade Area enhances Foreign Direct Investment inflows growth in Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka
- The Agreement on South Asian Free Trade Area entry into force in 2006
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation consists of:
- Muslims countries: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Maldives, and Pakistan
- Hindu: India
- Buddhist: Bhutan, Nepal, and Sri Lanka
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) belongs to:
- Central Eurasian Economic Area (Islamic Civilization)
- Buddhist Civilization
- Hindu Economic Area
Sample - South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) - Certificate of Origin
Sample - SAARC - Agreement on Services

Economic Corridors related to SASEC
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page










 WhatsApp
WhatsApp