Business in Malawi, Lilongwe, Blantyre
Malawian Economy, Logistics and Foreign Trade: agriculture, mining, manufacturing. Mzuzu (Malawi)
The Republic of Malawi: a landlocked agricultural country. Access via the Port of Maputo (Mozambique).
The economy of Malawi is based on the agricultural sector, which is the driving factor of the Malawian economic growth
- Malawi is the seventh largest world tobacco producer
- Malawi is Africa's third largest tea producer

- Introduction to the Republic of Malawi (East Africa)
- Malawian Economy
- International Trade of Malawi
- Export and Import Procedures
- Transport and Logistics
- Business and Investment Opportunities in Malawi
- Energy
- Services
- Food and Beverage
- Infrastructure
- Tourism
- Malawian Mining
- Manufacturing
- Forestry
- Case Study:
- Agriculture and Agro-processing sector in Malawi
- Malawian Mangoes
- Press Corporation Limited
- Access to the Malawian Market
- Business Plan for Malawi

The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Malawi” are:
- To analyze the Malawian Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in Malawi
- To explore the Malawian trade relations with the student's country
- To learn about Malawian Trade Agreements
- To develop a business plan for the Malawian Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Malawi” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate in African Business.

Master in Business in Africa, International Business, Foreign Trade.

Masters adapted to  Malawian Students.
Malawian Students.
Languages:  or
or  Malawi
Malawi  Malawi
Malawi  Malaui.
Malaui.
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in Malawi”: 1

International Trade, Logistics and Business in Malawi.

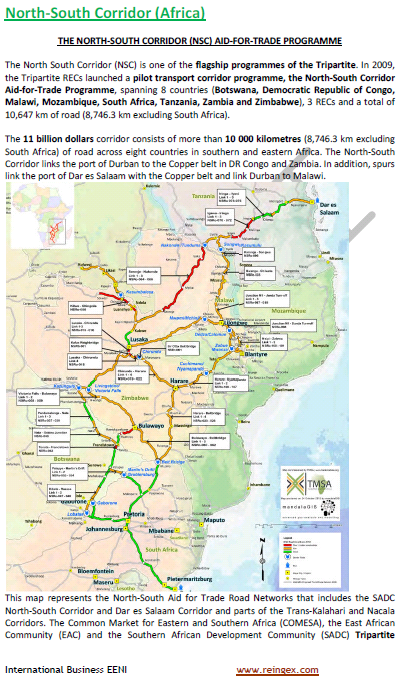
- North-South Logistics Corridor
- Nearest ports to Malawi
- Port of Maputo (Mozambique, 931 kilometers, Nacala Rail transport)
- Port of Dar es-Salaam (Tanzania): Malawi Cargo centre


Malawian Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Malawi and the East African Economic Area
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
- Southern African Development Community (SADC)
- European Union-SADC Agreement
- COMESA-EAC-SADC Agreement
- African Continental Free Trade Area
- The United States-Malawi
- European Union-Malawi
- Africa-EU Partnership
- GSP
- Trade Agreements with South Africa, Zimbabwe, Botswana, Mozambique
- Malawi-China Trade and Industry Agreement
- Malawi-India Trade Agreement
- ICGLR - Guest Member


- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention
- Hamburg Rules (Maritime Transport)
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- IMO- not a member

- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Union
- AU Convention on Combating Corruption
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Africa Agriculture Development Programme
- African Development Bank
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- Africa-Korea Partnership
- Africa-BRICS
- Africa-Turkey Partnership
- Afro-Arab Cooperation
- Arab Bank for Africa (BADEA)
- Africa-Japan Cooperation
- Africa-South America Summit
- China-Africa Cooperation
- Africa-India Cooperation

- United Nations
- Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)
- International Trade Centre
- World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO)
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
- World Health Organization
- Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency
- Commonwealth of Nations
- Borders of Malawi: Zambia, Tanzania, and Mozambique
- Population of Malawi: 18 million people
- Lilongwe (Political capital): 1.9 million people
- Blantyre (economic capital of Malawi): 1 million people
- The largest cities of Malawi are Lilongwe, Blantyre, Mzuzu and Zomba
- Malawian Life expectancy: 54.6 years
- Malawian Literacy rate: 72.8%
- The area of Malawi: 118,844 km²
- Independence of Malawi from the United Kingdom: 1964
More information about Malawi (EENI African Business Portal).
Religions in Malawi.
- African Traditional Religions
- Christianity
- Catholicism (2.3 million)
- Protestants (4 million, 35% of Malawian population)
- Islam (15%)

Malawi belongs to East African Economic Area.
Malawian Economy:
- Agriculture: 30% of Malawi's GDP
- The Malawian agricultural sector also grew strongly resulting in augmented tobacco production
- The Malawian economic growth impulse is generated by manufacturing, information and communication (IT), financial, and insurance services, mining, and quarrying, Transport and storage, accommodation, and food services sectors
- Malawian currency: Malawi Kwacha

International Trade of Malawi:
- International business and Foreign Direct Investment opportunities exist in all the sectors of the Malawian economy
- There are preference sectors that are targeted because of their economic potential to increase export earnings of Malawi, in line with the Malawi Growth and Development Strategy
- Main sectors offering optimum returns to local and foreign investors: manufacturing, agriculture, tourism, mining, and forestry
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page








 WhatsApp
WhatsApp