Business in Turkmenistan, Ashgabat, Turkmenbashi
Turkmen Economy and Foreign Trade, Logistics. Business in Ashgabat, Turkmenbashi (Turkmenistan) Petrol

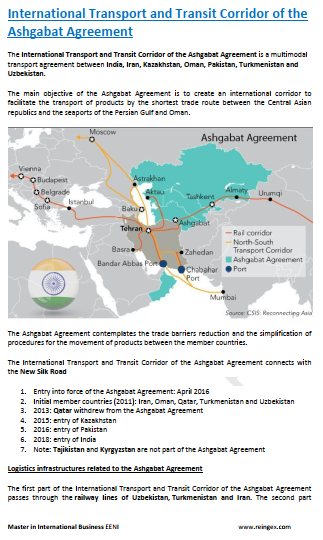
The Great Silk Road passes through Turkmenistan
Significant water resources (Karakum River)
Turkmen Mineral resources: hydrocarbon, mining, salt, boron, magnesium, potassium, rubidium, and bentonite
Drilling and exploration for petrol and gas
- Introduction to the Republic of Turkmenistan
- Turkmen Economy
- Economic Profile of the Regions of Turkmenistan
- Doing Business in Ashgabat
- Foreign Trade of Turkmenistan
- Transport and Logistics
- Business Opportunities in Turkmenistan
- Construction
- Textiles
- Energy
- Food industry
- Case Study:
- Awaza National Tourism Zone
- Gap Pazarlama (Textile)
- Access to the Turkmen Market
- Business Plan for Turkmenistan

The objectives of the subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Turkmenistan” are:
- To analyze the Turkmen Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in Turkmenistan
- To explore the Turkmen trade relations with the student's country
- To learn about Turkmen Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Turkmen companies
- To develop a business plan for the Turkmen Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Turkmenistan” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.


Masters adapted to  Turkmen Students.
Turkmen Students.
Languages:  (or
(or  Turkmenistán
Turkmenistán  Turkménistan).
Turkménistan).
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in Turkmenistan”: 1

International Trade, Logistics and Business in Turkmenistan.

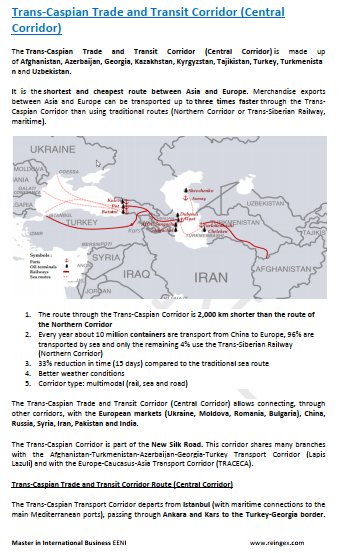
- Almaty-Bishkek Logistics Corridor
- Silk Road
- Corridor of the Ashgabat Agreement
- China-Central-West Asia Logistics Corridor
- Trans-Caspian Logistics Corridor
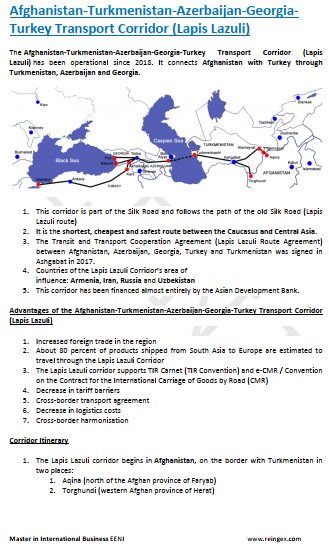
- Afghanistan-Turkey Logistics Corridor
- Transit and Transport Cooperation Agreement (Lapis Lazuli Route Agreement)
- Transport Corridor Europe-Caucasus-Asia (TRACECA) - is not a member, but has requested access
Sample: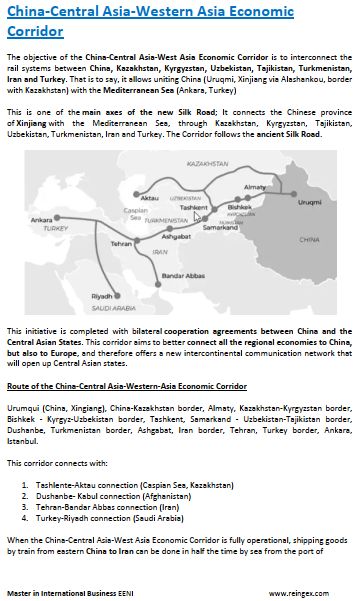

Turkmen Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Turkmenistan and the Central Eurasian Economic Area
- Economic Cooperation Organization (ECO)
- Central Asia Cooperation (CAREC)
- GSP
- Armenia-Turkmenistan Agreement
- Turkmenistan-Georgia Agreement
- Ukraine-Turkmenistan Agreement
- Russia-Turkmenistan Agreement
- Trade Agreement with the Eurasian Economic Union
- Islamic Trade Preferential System
- CIS (associated)
- SCO (Guest Attendance)

- World Trade Organization (WTO) - Government with observer status
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention
- Organization for Cooperation between Railways (OSJD)
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization
- International Road Transport Union (IRU)
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport

- Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC)
- Islamic Development Bank
- Asia-Middle East (AMED)
Euro-Asian Organizations:
- Boao Forum for Asia
- European Investment Bank
- Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE)
- Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- Economic Commission for Asia (ESCAP)
- Asian Development Bank
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue

- United Nations
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
- The Republic of Turkmenistan shares borders with Afghanistan, Kazakhstan, Iran, and Uzbekistan
- Turkmen Population: 5 million people
- 85% of the population are Turkmen
- Area of Turkmenistan: 491,000 km²
- Turkmen Capital: Ashgabat
- Official language of Turkmenistan: Turkmen (Turkic group of languages)
- English and Russian are widely spoken
- Territorial organization of Turkmenistan: five velayats (Ahal, Balkan, Dashoguz, Lebap, and Mary)
- Turkmen independence: 1991 (URSS)
- Turkmenistan is a Presidential Republic
Main religion: Islam.
Turkmenistan belongs to the Sunni-Turkic area of Islamic Civilization
Turkmen Economy.
- Agriculture: 80% of Turkmenistan is farm lands
- Turkmen industrial sector: petrol and gas, chemical, electric power, engineering, and textile (60 textile complexes)
- Main sectors of the Turkmen economy are petrol and gas, power engineering, agriculture, construction, transport and communications, chemical, textile, and building materials
- The Turkmenbashi complex of petroleum refineries is the largest high-octane gasoline and kerosene producer in Central Asia
- Gas pipelines to China and Iran
- Turkmen currency: Manat
- Turkmenistan is one of the ten most corrupt countries


International Trade of Turkmenistan.
International Trade and Business in Turkmenistan:
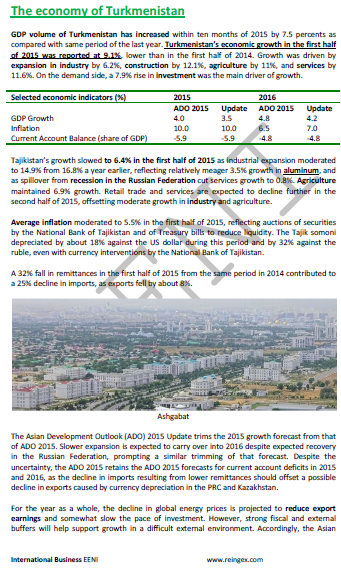
- Main exports of Turkmenistan are petroleum, carbon, cement, salt, iodine, and grains
- Turkmenistan is an Electricity exporter (Afghanistan, Iran, Turkey, and Tajikistan)
- Construction of the Kazakhstan-Turkmenistan-Iran Railway
- Regional transit centre (Rail transport)
Sample:
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp