Business in Moldova, Chisinau. Moldovan Economy
Moldova: one of the poorest European countries. Moldovan Foreign Trade, Logistics
The Republic of Moldova is one of the poorest countries in Europe with capita incomes similar to those of Nicaragua or Ghana
About 50% of Moldovans are engaged in agriculture (potatoes, cereals, sunflowers, vegetables, tobacco, wine, beer)
The Moldovan wine sector is growing considerably
- Introduction to the Republic of Moldova
- Moldovan Economy
- Doing Business in Chisinau
- Moldovan International Trade
- EU relations with Moldova
- Investment in Moldova
- Transport and Logistics
- Access to the Moldovan Market
- Business Plan for Moldova
Sample: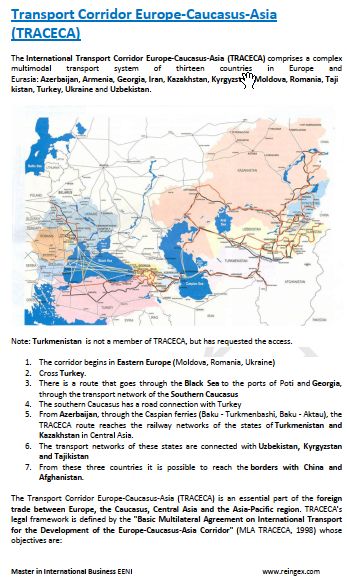

The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Moldova” are:
- To analyze the Moldovan Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in the Moldovan Market
- To research the trade relations of Moldova with the student's country
- To learn about Moldovan Trade Agreements
- To develop a business plan for the Moldovan Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Moldova” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:

Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.

Languages:  +
+  Moldavia
Moldavia  Moldavie
Moldavie  Moldávia.
Moldávia.
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in Moldova”: 1

International Trade, Logistics and Business in Moldova

- Europe-Caucasus-Asia Logistics Corridor
- Pan-European Transport Corridor IX (Finland-Greece)
- Access to the Trans-Caspian Trade and Transit Corridor (Central Corridor)

Moldovan Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Moldova and the Orthodox Economic Area
- Central European Free Trade Agreement (CEFTA)
- Commonwealth of Independent States
- Organization for Democracy and Economic Development (GUAM)
- Black Sea Economic Cooperation
- Central European Initiative
- Ukraine-Moldova Agreement
- Armenia-Moldova Agreement
- Turkey-Moldova Agreement
- Kyrgyz Republic-Moldova Agreement
- Trade Agreements with Azerbaijan, Georgia, and China
- Regional Cooperation Council
- European Union-Moldova
- UK-Moldova Free Trade and Economic Integration Agreement
- Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) - Observer country
Sample:

- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention
- Organization for Cooperation between Railways (OSJD)
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization (IMO)
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- Customs Convention on Containers
- CMR Convention
- International Road Transport Union (IRU)
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport

European Trade and Economic Organizations of Moldova
- Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE)
- Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)
Global Organizations:
- United Nations
- Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)
- International Trade Centre
- World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO)
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
- Capital of Moldova: Chisinau
- Moldovan Official Language: Romanian
- Moldovan Area: 33,851 km²
- Moldovan Population: 3.6 million people
- Type of Government of Moldova: Parliamentary Republic
- Borders of Moldova: Romania and Ukraine
- Moldova is a landlocked country
- Moldovan Independence: 1991 (Soviet Union)
Religion in Moldova: Orthodoxy (Romanian Orthodox Church) (Christianity).
Moldova belongs to the Orthodox Economic Area
Economy of Moldova.
- Moldovan GDP (nominal): 14,820 million dollars
- GDP per capita of Moldova: 4,177 dollars
- Currency of Moldova: Moldovan Leu
- Main Moldovan products are wine, sugar, agricultural machinery, refrigerators, textiles, building materials
- Moldova has applied for a membership to the European Union
- According to the Index of Economic Freedom, Moldova occupies the 110th place in the world
Sample: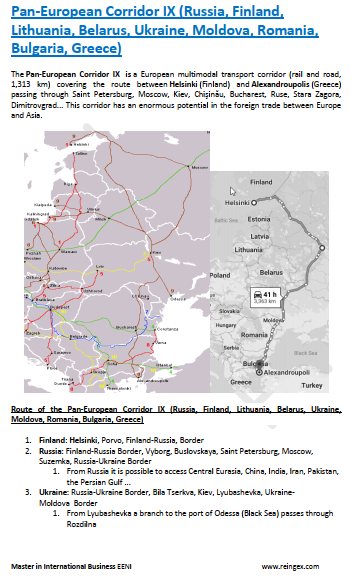

Moldovan Foreign Trade.
- Main Moldovan Exports are foods, textiles, machinery
- Top export markets of Moldova: Russia (26%), Romania, Italy and Ukraine
- Main Moldovan Imports are mineral products and fuels, machinery and equipment, chemical products, textiles
- Main suppliers of Moldova: Russia (14%), Romania, Ukraine and China
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp

