Business in Belarus, Minsk, Brest, Vitebsk
Foreign Trade of Belarus, Logistics. Economic Profile. Union State with Russia

Union State (Russia and Belarus). The Strategic Partnership with the Russian Federation stems from their location, historical and Cultural links between Russia and Belarus, economic ties and cooperation between Belarusian and Russian companies
Main trade partners of Belarus are Russia, Ukraine, the Netherlands, Germany, Poland, Venezuela, the UK, Latvia, and Italy
Potash fertilizer and flax fiber production are the largest export products of Belarus
- Introduction to the Republic of Belarus (Europe)
- Belarusian Economy
- Economic Profile of the Belarusian regions: Brest, Vitebsk, Gomel, Grodno, Mogilev
- International Trade of Belarus
- The Union State (Russia and Belarus)
- European Union-Belarus Trade Relations
- Doing Business in Minsk
- Case Study:
- Gomselmash Company
- Spartak
- Transport and Logistics
- Access to the Belarusian Market
- Business Plan for Belarus

The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Belarus” are:
- To analyze the Belarusian Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in Belarus
- To explore the Belarusian trade relations with the student's country
- To learn about Belarusian Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Belarusian companies
- To develop a business plan for the Belarusian Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Belarus” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:

Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.

Languages:  (
( Bielorrusia
Bielorrusia  Belarus).
Belarus).
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in Belarus”: 1

Мастер в Международном Бизнесе.
Masters adapted to  Belarusian Students.
Belarusian Students.
International Trade, Logistics and Business in Belarus.

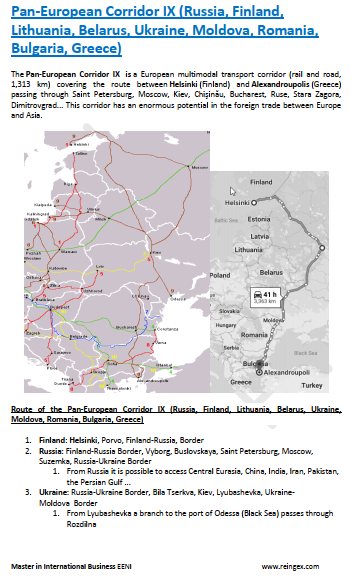

Belarusian Trade Agreements and market access:
- Belarus and the Orthodox Economic Area
- Commonwealth of Independent States
- Free Trade Area (CISFTA)
- Eurasian Economic Union
- EAEU-Vietnam Agreement
- Central European Initiative
- Belarus-Kazakhstan-Russia-Ukraine Common Economic Space
- Trade Agreement between Russia, Belarus, and Kazakhstan
- Belarus-Russia-Ukraine Agreement
- Russia-Belarus-Kazakhstan Customs Union
- Ukraine-Belarus Agreement
- European Union-Belarus
- EU Eastern Partnership
- European Neighborhood Policy
Ukraine is an observer country
- SCO
- Association of Caribbean States (ACS)
- Council of the Baltic Sea States Latin American Integration Association (LAIA)
Ukraine was an observer country at the Eurasian Economic Community (EurAsEC) - Succeeded by the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU).

- WTO (in process of accession)
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention
- Convention on the Harmonization of Frontier Controls of Goods
- Organization for Cooperation between Railways
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization (IMO)
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- Customs Convention on Containers
- CMR Convention
- International Road Transport Union (IRU)
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport

European Organizations:
- Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)
- Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE)
- European Investment Bank
Global Organizations:
- United Nations
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
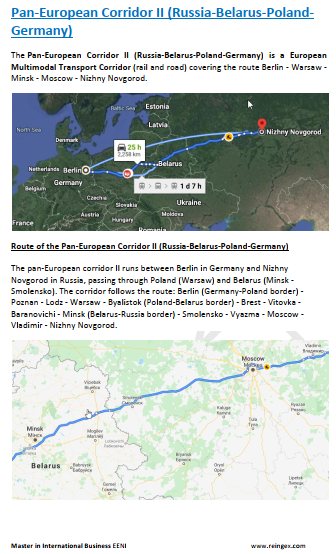
- Belarus share frontiers with Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Russia, and Ukraine
- The capital of Belarus is Minsk (3 million inhabitants)
- Belarusian population: 9.6 million people
- The spoken languages in Belarus are Belarusian and Russian
- Government Type: Presidential Republic
- Belarus gained the independence from the Soviet Union in 1990
- Belarusian Area: 207,600 km²
The Belarusian main religion is Orthodox Christianity. There are 1.7 million Catholics.

Belarus belongs to the Orthodox Economic Area.

Belarusian Economy.
- The Republic of Belarus has benefited a strong economic growth since its independence in 1992
- The European Union has suspended the economic partnership with Belarus until the political and civil conditions improve
- The majority of Foreign Direct Investment came from the EU (43%) and Russia (33%)
- The largest Foreign Direct Investment sources were Russia (82%), Switzerland, Cyprus, and Germany
Minsk is the capital and industrial centre of the Republic of Belarus.
- Main economic activities of Minsk are industry (20% of the total industrial production volume of Belarus), construction, science and scientific services, food production, light and motor industry, tractor manufacturing, machine tool, construction, metal working, instrument making and radio engineering and electronic equipment manufacturing
- Minsk export 60% of his production
- Main industrial export products are tractors, lorries, metal-working machine tools, refrigerators, TV sets, motor-cycles, and bicycles
- Main export market destination are Russia, Ukraine, Baltic States, Poland, Germany, Pakistan, and Kazakhstan
- Access to the Eurasian Land Transport Initiative
International Trade and Business in Belarus:

(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp