E-business and Foreign Trade. Global E-commerce
E-commerce: selling through electronic systems such as the Internet

Global Marketing - Distribution
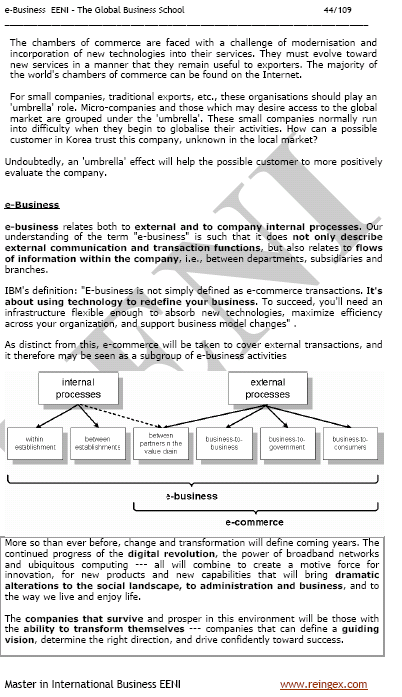
E-business (electronic business) refers to the use of digital technologies to conduct a wide range of business activities and transactions online. It goes beyond just buying and selling goods, encompassing processes such as supply chain management, human resources, customer service, and production. By leveraging the internet, e-business enhances operational efficiency, enables access to global markets, and reduces reliance on traditional intermediaries.
E-commerce refers to the buying and selling of Products or services through electronic systems such as the internet and other computer networks. It encompasses a broad range of technologies and tools that facilitate online transactions, including mobile shopping platforms and secure online payment systems.
Digital entry is a market entry strategy that leverages digital platforms—such as e-commerce, mobile apps, and social media—to establish a presence in a new market, bypassing the need for physical infrastructure.
- Digitalization and e-business
- Distribution and e-Business.
- Case Study: Amazon – Global Distribution Powered by E-Business
- Business Models on the Web: B2B, B2C, B2A, B2E
- E-commerce and Digital Entry
- Case Study: Warby Parker — Digital Entry Disrupting the Eyewear Industry
- Case Study: Dell Technologies’ Hybrid Distribution Strategy
- Digital Distribution
- Case Study: Netflix and the Transformation of Digital Distribution in Entertainment
- E-Processes (CRM, SCM, e-Procurement...)
- E-Security (Digital Signature, SSL Protocol, Secure Electronic Transactions)
- Religious influencers and business
- Case Study: The Fashion Influencer Huda Kattan
- Case Study:
- Teleworking and e-business
- Amazon
- Alibaba Group
- Online Nigerian retail sites
- Legislative texts related to Electronic Commerce,
United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL).
- UNCITRAL Model Law on Electronic Commerce
- UNCITRAL Model Law on Electronic Signatures
- United Nations Convention on the use of Electronic Communications in International Contracts
The objectives of the subject “e-Business” are the following:
- To understand the concepts of e-business, e-commerce, digital entry, and digital business models that a company can deploy, as well as the importance of strategy, Marketing and technology in an e-business project
- To analyze the concept of security in e-business and how to improve it through some security systems. The characteristics of digital signatures and encryption systems will be discussed in detail
- To introduce the student to the basic tools for creating a web presence and learn how to use them
(E-business):

The Subject “E-business and Foreign Trade. Global E-commerce” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
- Masters: Foreign Trade, International Business
- Doctorate: World Trade
- Course: Advanced Global Marketing
Languages:  or
or  EENI
EENI  e-business.
e-business.
- Subject Credits “e-business”: 4

- Duration: 4 weeks
E-business is a new way of doing business that can become a competitive advantage for a company in the global marketplace if can design an e-business strategy in line with the strategy of Internationalization.
In many cases, this lack of strategy can convert this advantage into a threat or a weakness for the company.
Types of E-commerce
- B2C (Business to Consumer): Businesses sell products or services
directly to individual consumers.
Example: Amazon, Zara's online store. - B2B (Business to Business): Transactions take place between businesses,
such as manufacturers selling to wholesalers or retailers.
Example: Alibaba. - C2C (Consumer to Consumer): Consumers sell goods or services to other
consumers via third-party platforms.
Example: eBay, Etsy. - C2B (Consumer to Business): Individuals offer products or services to
businesses, often on a freelance or contract basis.
Example: Influencer marketing, user-generated content platforms.
Warby Parker is a strong example of successful digital market entry in the eyewear industry. Rather than launching through traditional retail channels, the company began as an online-only Brand, offering a home try-on program that provided customers with convenience, affordability, and transparency. This digital-first approach allowed Warby Parker to disrupt the market effectively. Over time, the company expanded into physical retail, creating an integrated omnichannel experience that blends online convenience with in-person service.
Dell initially rose to prominence through its direct-to-consumer (DTC) model, selling custom-built PCs online and via telephone, thereby bypassing traditional retailers. This approach allowed Dell to offer competitive Pricing and build strong customer relationships. However, as global demand increased, enterprise needs evolved, and competition intensified, Dell transitioned to a hybrid distribution model—combining direct sales, indirect partnerships with resellers and Distributors, and robust online channels to reach a broader customer base.
Amazon's success illustrates how e-business can drive global distribution—and how global distribution, in turn, sustains scalable e-business. The company’s model demonstrates that seamless integration between digital platforms and physical logistics infrastructure is essential for enabling international expansion and operational efficiency.
Globalization of the World Economy and fast growth of e-business create new opportunities for International Traders. However, they bring in their Risks as well.
Enterprises need expertise to be able to face internationalization and defiance of e-business, as well as learn principles of the new Economy. This subject is ideal for businesspeople, export managers, International Trade managers, students, professors, consultants and many other people and enterprises wishing to develop their online business successfully.
Internet, e-commerce, e-business, digital marketing, etc. - you hear these words more and more often as these phenomena more and more become a part of daily business all around the world. enterprises start selling online and change their internal structure. Digitalization is a key concept in e-Business. While the concept may be fundamental the impact on business will be phenomenal. New governmental and business models are being developed as a result. If implemented correctly digitalization can positively contribute to social and economic structures in both the developed and less developed countries.
We are moving from an industrial to an information society, governed by the New Economy - The digital or e-economy. New opportunities and new threats are emerging. Small players can compete with big ones as long as they can find their market niche. Many concepts that were valid in traditional, bricks and mortar world will need to be reinvented taking into account the digital world potential. Somehow, this is all having an impact on society. In order to meet digital defiance, enterprises must fully understand the nature of the new e-economy.
Nobody has total security on the Internet, meaning that both buyers and sellers run some risk. However, developments in technology offer a means of making transactions that are becoming increasingly safer. Data encryption techniques can make e-commerce more secure than traditional credit card trading. The difficulty lies in convincing digital consumer that our site is secure and that electronic trading is also perfectly safe. When a transaction is made on the Internet, and one's personal data is sent (name, address, credit card number, etc.) we should consider whether it may be intercepted in the transmission (between the buyer and seller) by anyone else.
Could anyone use this information to take on our identity? At the same time, the seller wishes to ensure that the data he receives is genuine, or in other words; he needs to know that the purchaser is who he “says” he is. It is for these reasons that “secure transmission systems” have been developed.

(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page












 WhatsApp
WhatsApp