Business in South Sudan. Juba, Oil (60% of GDP)
South Sudanese Agriculture, Oil sector, Infrastructures (Foreign Trade, Logistics)
The Republic of South Sudan: The newest country in the World (Independence from Sudan in 2011).
- Top South Sudanese sector: agriculture (80% of the employment)
- South Sudanese petrol sector: 70% of Government revenues, 60% of GDP (direct exports)

- Introduction to the Republic of South Sudan (East Africa)
- Business in Juba
- Economy of South Sudan
- South Sudanese Agriculture Sector
- International Trade of South Sudan
- Transport and Logistics
- Business and Investment Opportunities in South Sudan
- Agribusiness
- Infrastructure
- Tourism and Hospitality
- South Sudanese Mining
- Petroleum (Oil)
- South Sudan Investment Authority
- Access to the South Sudanese market
- Business Plan for South Sudan
International Trade and Business in South Sudan:


The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in South Sudan” are:
- To analyze the South Sudanese Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in South Sudan
- To explore the South Sudanese trade relations with the student's country
- To learn about South Sudanese Trade Agreements
- To develop a business plan for the South Sudanese market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in South Sudan” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate in African Business.

Master in Business in Africa, International Business, Foreign Trade.

Languages:  (
( Soudan du Sud
Soudan du Sud  Sudão do Sul
Sudão do Sul  Sudán del Sur).
Sudán del Sur).
Credits of the Subject “Doing Business in South Sudan”:
1 
International Trade, Logistics and Business in South Sudan.

- The Northern Logistics Corridor links with South Sudan
- Access to the Port of Mombasa
Sample: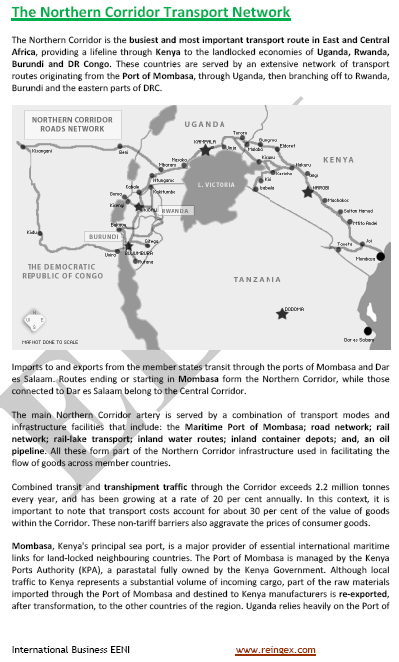

South Sudanese Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- South Sudan and the East African Economic Area
- IGAD (Intergovernmental Authority on Development)
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
- East African Community (EAC)
- Nile Basin Initiative
- Conference on the Great Lakes
- United States - AGOA
- GSP “Everything But Arms” agreement

- WTO (in process of accession)
- Is not a member of the
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention
South Sudan is a member of:
- African Union
- AU Convention on Preventing and Combating Corruption (not signed)
- United Nations
- UNCTAD - Not-member
- Africa-South America Summit
- Negotiations with the Commonwealth of Nations, IMF, WB, WTO
- The Republic of South Sudan is the newest country in the Word (2011)
- South Sudan is a Landlocked country
- Borders of South Sudan: The Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Kenya, Uganda, and Sudan
- South Sudanese Population: 12.2 million.
- 72% of the South Sudanese population under thirty years
- Area of South Sudan: 644,329 km²
- Capital of South Sudan: Juba (250,000 inhabitants)
- South Sudanese official language: English
- Local languages: Bari, Dinka, and Murle
- Independence of South Sudan from Sudan in 2011
More information about South Sudan (EENI African Business Portal).
Religions in Sudan
- Christianity (60% of the population)
- African Traditional Religions
South Sudan belongs to East African Economic Area.

South Sudanese Oil sector: 60% of GDP.
- Political instability in South Sudan
- Opportunities related to the Nile River: energy production and fishing industry
- Business Opportunities: petroleum (oil), agriculture, mining, infrastructure, and energy
- Kenya is a key player in South Sudan
- The Port of Mombasa (Kenya) is the main Import/Export port of South Sudan
- Top South Sudanese export products: petroleum and natural resources
- Top South Sudanese trading partners: China, Japan, the United States, Uganda, and Kenya
- Currency: South Sudanese Pound (SSP)
- Internet code (ISO): ss
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page







 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
