European Central Bank. Monetary Union (EU)
Eurozone. European Central Bank. EU Economic and Monetary Union
- Introduction to the European Central Bank (EU): the central bank of the world's second largest economy
- The European Central Bank and the Economic and Monetary Union
- Eurozone
- Convergence Criteria
- Monetary stability and the European Central Bank
- European financial system supervision
- Structure of the European Central Bank
- Roles of the European System of Central Banks (ESCB) and the Eurosystem
- Independence of the European Central Bank
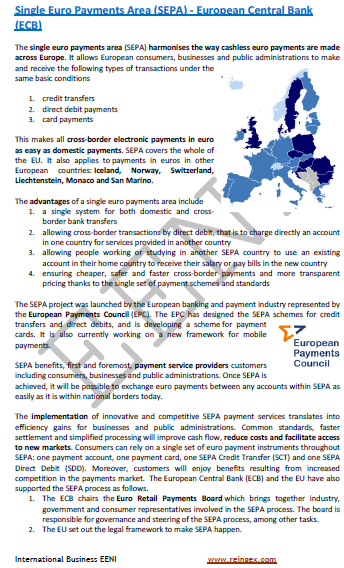
- Single Payments Area in Euros
- Europe 2020 strategy
Sample - European Central Bank:

The educational aims of the Subject “European Central Bank (ECB)” are the following:
- To understand the role of the European Central Bank in the financial and monetary stability of the European Union
- To understand the EU Economic and Monetary Union (EMU)
- To study the convergence criteria of the Eurozone
- To understand the importance of the Eurozone
- To analyze the implications for the Eurozone Countries

The Subject “European Central Bank” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:

Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.


Languages:  or
or  Banco Central Europeo
Banco Central Europeo  Banque centrale européenne
Banque centrale européenne  Banco Central Europeu.
Banco Central Europeu.
Credits of the Subject “European Central Bank”: 1 

The nineteen countries of EU that have adopted the Euro as common currency are part of the European Central Bank (ECB) whose main objective is to implement a price stability policy in the Eurozone, seeking to maintain the purchasing power of the euro.
In 1999, the Eurozone and the European Central Bank were established by eleven EU countries (Germany, Austria, Belgium, Spain, Finland, France, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands and Portugal), transferring all their monetary policy powers to the European Central Bank.
Subsequently, the euro area has been expanding:
- 2001: Greece
- 2007: Slovenia
- 2008: Cyprus and Malta
- 2009: Slovakia
- 2011: Estonia
- 2014: Latvia
- 2015: Lithuania
Except for Denmark, they have an obligation to adopt the Euro in compliance with the so-called convergence criteria of the European Union.
- The European Union countries that have not yet adopted the Euro are Bulgaria, Croatia, Hungary, Poland, the Czech Republic, Romania and Sweden
- The European Central Bank is the only institution that can authorise the issuance of the euro banknote
- The headquarters of the European Central Bank is in Frankfurt (Germany)
- United Kingdom (non-EU member, BREXIT)
All the central banks of the countries that have adopted the euro form the so-called Eurosystem. The European Central Bank (ECB) is the key institution of EU's Eurosystem and the Single Supervisory Mechanism (control of EU credit institutions).
The main body of the European Central Bank is the Governing Council, made up of six members of the Executive Committee and the directors of the nineteen central banks of the Eurozone. Its main mission is to design the Eurozone monetary policy, as well as banking supervision.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp