Foreign Direct Investment (FDI, Outlook)
Expropriation risks. Foreign Direct Investment, Delegations
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) refers to an investment made by a firm or individual from one country into business interests in another country, with the intention of establishing a lasting presence and exerting significant control over the foreign enterprise. This typically involves ownership of assets, setting up Subsidiaries, or acquiring stakes in existing businesses.
The Subject “Foreign Direct Investment” consists of three parts:
1- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
- Introduction to Foreign Direct Investment
- Types of FDI
- Greenfield Investment
- Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A)
- Joint Ventures and Strategic Alliances
- Case Study: Toyota’s Foreign Direct Investment in the United States
- Case Study: Mining Industry and Resource-Seeking FDI in Africa (The Case of Rio Tinto in Guinea)
- Global Investment Outlook
- The World Trade Organization (WTO) of Foreign Direct Investment
- Agreement on Trade-Related Investment Measures (TRIM)
- OECD of Foreign Direct Investment
- The European Union policy on Foreign Direct Investment
- The Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA)
- Index of Economic Freedom (Heritage)
- FDI and Developing Countries
2- Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) and Foreign Direct Investment.
- Introduction to the UN Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)
- Index of Foreign Direct Investment
- Inward and outward Index. Methodology
- World Investment Report
- Establishing enterprises abroad: sales delegations, affiliated enterprises, branches, and joint ventures
- Optimizing expropriation Risks
- Corporate governance
- Investing in Developing Countries
- Case Study: Reconstruction of an industry in the former Soviet Republics
Sample - Foreign Direct Investment (FDI):
The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Direct Investment” are the following:
- To offer a global vision of Foreign Direct Investment
- To understand the role of the UN Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)
- To learn different strategies to establish a company abroad
- To know how to analyze Foreign Direct Investment flows
On finishing this subject, student will know:
- Different strategies to follow to set up a company in an international market beyond merely sale of Products
- Legal formulas that adapt better to investments
- To analyze decisions taken by a company that established its commercial branch in the United States
- Troubles are arising from establishing investments in Developing Countries

The Subject “Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Master: International Business.


Postgraduate Certificate in Global Marketing.

Languages:  or
or  Investissement direct à l’étranger
Investissement direct à l’étranger
 Inversión extranjera directa.
Inversión extranjera directa.
- Subject Credits “Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)”: 3

Key Characteristics of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
- Lasting Interest: Typically involves ownership of at least 10% of the voting stock or shares in a foreign company, indicating a long-term commitment.
- Control and Influence: Unlike passive investments, FDI allows the investor to influence or participate in management decisions, operations, and strategic direction.
- Cross-Border Movement: Involves the transfer of capital, technology, managerial expertise, and sometimes labor across national borders.
FDI vs. Portfolio Investment:
FDI differs from portfolio investment, where investors purchase foreign securities—such as stocks or bonds—purely for financial returns, without seeking control or involvement in the business.
Measuring Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
- FDI Inflows: The amount of foreign investment received by a country during a specific period, typically a year.
- FDI Stock: The total accumulated value of foreign investment present in a country at a given point in time.
- Balance of Payments: FDI transactions are recorded under the financial account in a country’s balance of payments statistics, reflecting cross-border capital movements.
Emerging markets have become major recipients of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) due to their high growth potential, expanding consumer bases, and opportunities for cost-effective production.
The Economic Cooperation and Development recommends that a Foreign Direct Investment company can be defined as “an incorporated (or unincorporated) company in which a foreign direct investor owns 10% or more of shares (or voting power)”.
Toyota Motor Corporation, a premier Japanese automaker, ranks among the
world's largest multinational corporations. During the 1980s and 1990s, Toyota
significantly expanded its foreign direct investment (FDI) in the United States,
establishing manufacturing facilities and regional headquarters. This case
examines the motivations, impacts, and challenges of Toyota’s FDI in the US.
The Economic Cooperation and Development analyses global statistics on Foreign Direct Investment. OECD Guidelines for Multinational enterprises are suggestions addressed by Governments to multinational corporations.
The Agreement on Trade-Related Investment Measures (“TRIM Agreement”), one of the Multilateral agreements on trade in products, forbids International Trade-Related Investment measures (local content requisites).
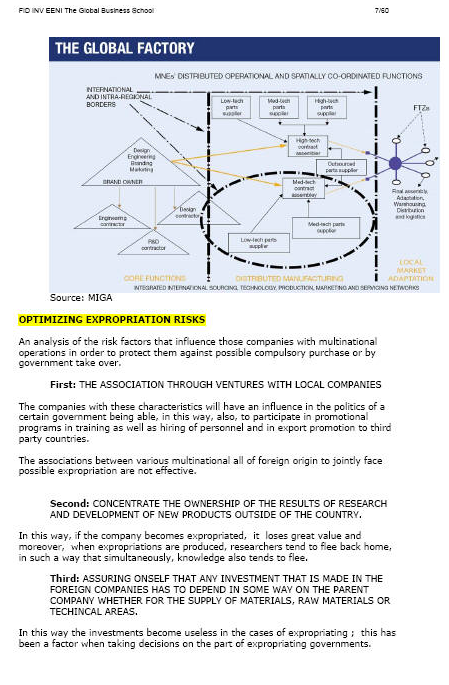
The mission of the Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA) (World Bank Group) is to promote Foreign Direct Investment in Developing Countries to help support economic growth, poverty reduction and improve lives of people.
Sample: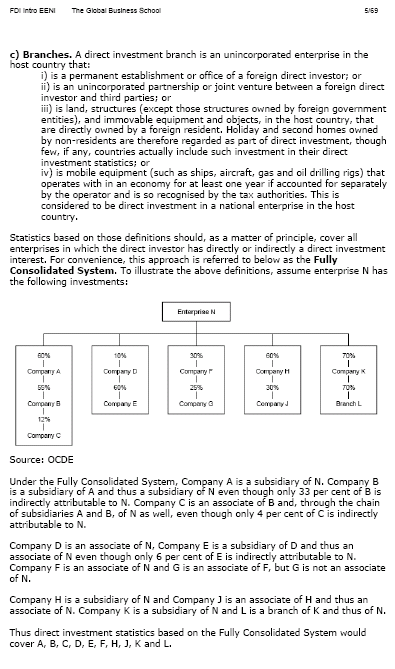
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page










 WhatsApp
WhatsApp