Course: European Single Market
Course “European Single Market” (e-learning, 4 ECTS,  )
)

The main objective of the Professional Course “European Single Market” taught by EENI Global Business School, is to analyze the complex functioning of the European Single Market so that companies can take full advantage of the enormous opportunities that the single market offers both to trade in products and services.
 Enrol / Request for Information
Enrol / Request for Information

- Credits: 4

- Duration: 1 month It is recommended to dedicate about twelve hours of study per week following a flexible schedule. It is possible to reduce the duration dedicating more hours a week
- Tuition Fees: EUR 96
- Open Online Enrollment
- Download the syllabus of the Course (PDF)
Course intended for all those who need to understand the advantages of the European Single Market for their business.
Learning materials :  .
.
- Also available in For improving the international communication skills, the student has free access to the learning materials in these languages (free multilingual training).
 Curso Mercado Unico UE
Curso Mercado Unico UE  Cours marché unique européen
Cours marché unique européen  Curso Mercado Único de UE
Curso Mercado Único de UE

This course contains exercises that are evaluated, which the student must work out and pass to obtain the Diploma of the Professional Course: “European Single Market” issued by EENI Global Business School.
Students who have taken this course can validate and register for a Master or Doctorate at EENI.
This course belongs to the following Higher Education Programs taught by EENI:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Doctorate: European Business, World Trade.
Masters for the Students from the  EU.
EU.
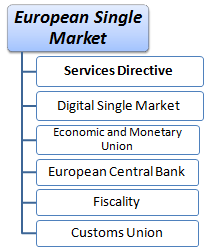
1- European Single Market: principle of free movement of persons, services, capital and goods.
2- Services Directive of the EU Single Market: elimination of all barriers to the intra-European trade in services and restrictive requirements in the Single Market.
3- Digital Agenda for Europe: towards a safe and free European Digital Single Market.
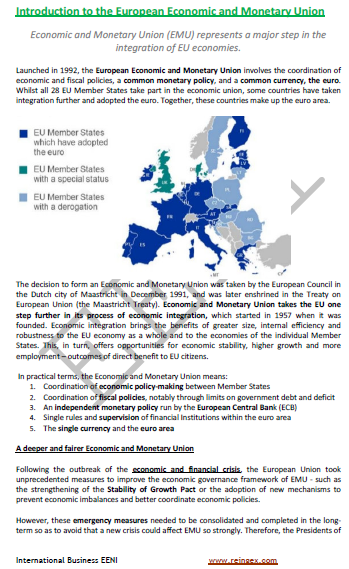
4- Economic and Monetary Union: the Monetary Policy of the EU
5- Role of the European Central Bank (ECB): the central bank of the second largest world economy and issuer of the Euro
6- Customs Union of the EU: a common policy on imports from the third countries.
7- Taxation in the Single Market: the Fiscal Policy of the EU and taxes in the single market.


- Atlantic Corridor
- Baltic-Adriatic Corridor
- North Sea-Baltic Corridor
- North Sea-Mediterranean Corridor
- Mediterranean Transport Corridor
- Eastern Europe-Eastern Mediterranean Transport Corridor
- Scandinavian-Mediterranean Transport Corridor
- Rhine-Alpine Transport Corridor
- Rhine-Danube Transport Corridor
- Strasbourg-Danube Transport Corridor
- Pan-European Corridor II
- Pan-European Corridor IX

The specific aims of the Course are the following:
- To understand the importance and functioning of the European Single Market
- To analyze the principles of free movement of people, services, capitals and goods within the EU Single Market
- To understand the Competition Policy that the EU applies within the single market
- To understand the importance of the EU Services Directive in the functioning of the Single Market and how to take advantage of this directive
- To identify the Barriers to trade in services in the EU
- To analyze the EU Electronic Commerce Directive
- To understand the concept of the European Digital Single Market
- To analyze the benefits to the EU, countries, businesses and citizens of the EU single digital market
- To understand the pillars of the European Economic and Monetary Union and the role of the related institutions
- To understand the key role of the European Central Bank
- To understand the importance of the Eurozone
- To understand the principles of the EU Monetary Policy as well as the financial assistance mechanisms
- To know the functioning of the supervision of the Eurozone
- To learn the convergence criteria
- To analyze the pillars and functioning of the Customs Union of the EU
- To know the new Customs Code of the EU
- To know the principles of the Fiscal Policy of the EU, Taxation in the Single Market and general rules on VAT in the EU
The Single market completion (free movement of people, services, capital and goods) is one of the major achievements of the EU, although the Europe 2020 Strategy has been designed to achieve it fully. For trade in goods, the single market is a reality, but it is not so much for trade in services, where many Technical Barriers to Trade persist.
The Services Directive was introduced precisely to remove all the trade barriers in the intra-European services.
With the aim of facilitating the online access to products and services and relaunching the European economy, the European Commission published the Strategy for the creation of a European Digital Market.
One of the European Single Market foundations is the Economic and Monetary Union. Five European institutions, led by the European Central Bank, define the EU Monetary Policy, issue of the euro as well as the price stabilization mechanisms in the euro area.
Any company wishing to do business in the countries of the EU must know the implications of the Customs Union, especially to analyze the competitiveness of its product related to the third countries.
Notes:
- Germany, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Denmark, France, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Estonia, Finland, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, the Czech Republic, Romania and Sweden are members of the European Single Market
- Germany, Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Portugal and Slovenia are part of the euro area
Knowledge Area: Europe.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



